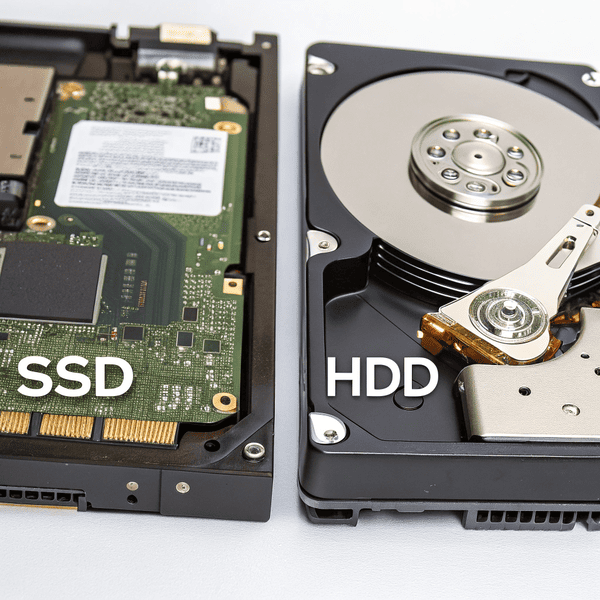
You want faster boot times, fewer system crashes, and reliable storage. Picking between old hard drives and new SSDs gets confusing if you don’t know the facts.
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are storage devices that use Solid-state drives (SSDs)[^1] are storage devices that use flash memory instead of spinning disks, making them much faster and more durable than traditional hard drives.
[^1]: Explore this link to understand how SSDs can enhance your device’s performance and reliability.
instead of spinning disks, making them much faster and more durable than traditional hard drives.
Solid-state drives changed storage forever. Still, you might wonder what makes them special, if they really beat HDDs, or what “enterprise SSD” really means. In this post, I’ll clear up the confusion. You’ll get short answers, real insights, and see why pros are switching for good.
What are solid-state drives?
Old hard drives make noise and break down. You want storage that’s silent, fast, and tough enough for daily use.
Solid-state drives (SSDs) use flash memory chips[^1] to store data. They work with no moving parts, so they load files and apps quicker and don’t wear out like spinning HDDs.
[^1]: Learn about the technology behind flash memory chips and their role in enhancing SSD performance.
use flash memory chips to store data. They work with no moving parts, so they load files and apps quicker and don’t wear out like spinning HDDs.
To give a clearer picture, think of SSDs as a giant, super-fast USB stick hidden inside your device. They read and write data at lightning speeds. Because there are no moving parts—like spinning platters or read heads—they’re immune to shocks and don’t create heat or noise. This makes them the ideal solution for laptops, desktops, and even professional cameras.
Here’s a basic comparison table:
| Feature | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Tech | Flash memory | Spinning disks |
| Moving Parts | None | Yes |
| Speed | Very high | Slower |
| Durability | High | Susceptible to shock |
| Noise | Silent | Audible noise |
| Form Factor | Thin, compact | Larger/heavier |
Switching to SSDs is one of the easiest ways to make any computer run like new.
Is solid-state better than HDD?
I used to use HDDs for everything, but they wore out fast and boot times dragged. Is switching really worth it?
Yes. Yes. Solid-state drives are better than HDDs[^1] in speed, reliability, durability, and power use. They make computers boot faster, open programs instantly, and last longer under regular use.
[^1]: This resource will provide insights into the limitations of HDDs and how they compare to Solid-state drives.
are better than HDDs in speed, reliability, durability, and power use. They make computers boot faster, open programs instantly, and last longer under regular use.
Dive a little deeper and the reasons are obvious. SSDs can start Windows or MacOS in a few seconds, compared to a minute or more for HDDs. They copy files many times faster. Plus, because they handle physical shocks better, laptops with SSDs almost never suffer from dropped-drive failures.
There are still situations where you might pick HDDs—for example, when you want cheap, huge storage (like for backups). HDDs win on dollars per terabyte, but for day-to-day computing or demanding tasks, SSDs crush the old drives every time.
| Attribute | SSD | HDD |
|---|---|---|
| Boot Time | ~5-10 seconds | ~30-60 seconds |
| Read/Write Speed | 500MB/s to 7,000MB/s+ | 50-200MB/s |
| Energy Use | Low | Higher |
| Typical Lifespan | 5+ years | 3-5 years |
In my experience, upgrading from HDD to SSD always feels like buying a brand-new machine.
What is an enterprise SSD?
Home computers are easy—but when you manage big business servers or large amounts of data, you need unbeatable reliability. So, what makes an SSD “enterprise” grade?
An enterprise SSD is a solid-state drive designed for servers or data centers. It offers high endurance, consistent performance under load, and extraAn enterprise SSD[^1] is a solid-state drive designed for servers or data centers. It offers high endurance, consistent performance under load, and extra data-protection features.
[^1]: Explore this link to understand how enterprise SSDs enhance performance and reliability in data centers.

Enterprise SSDs differ from normal SSDs in a few ways. They’re engineered to handle being written to all day, every day—far more than a regular user drive. Manufacturers add things like end-to-end data protection, power-loss circuitry to avoid sudden crashes, and strong error correction. Most come with long warranties and are tested for 24/7 operation.
There are levels of enterprise SSDs, marked for “read intensive” (RI), “mixed use” (MI), or “write intensive” (WI) workloads. For example, a database that gets constant updates needs WI, while a reporting server may only need RI.
| Enterprise SSD Feature | Why it Matters |
|---|---|
| High endurance rating | Handles years of heavy writes |
| Power-loss protection | Prevents data loss in outages |
| Consistent performance | Stays fast even under stress |
| ECC & firmware upgrades | Catches and fixes more errors |
| Warranty and support | Usually 5 years, business hours |
When uptime, data safety, and long life matter most—enterprise SSDs justify their price.
Conclusion
Solid-state drives change how we store data. SSDs beat HDDs in speed and dependability. For critical jobs, enterprise SSDs are the gold standard every business should invest in.